§Using the Play console
§Launching the console
The Play console is a development console based on sbt that allows you to manage a Play application’s complete development cycle.
§Launching the console using Typesafe Activator
The preferred method for launching the Play development environment when using Typesafe Activator is using the in built browser based UI. However, if you would prefer to use a console based environment, then change to the application directory, and run activator.
You may need to ensure that your Activator installation directory is in your system PATH.
§Launching the console using Play standalone
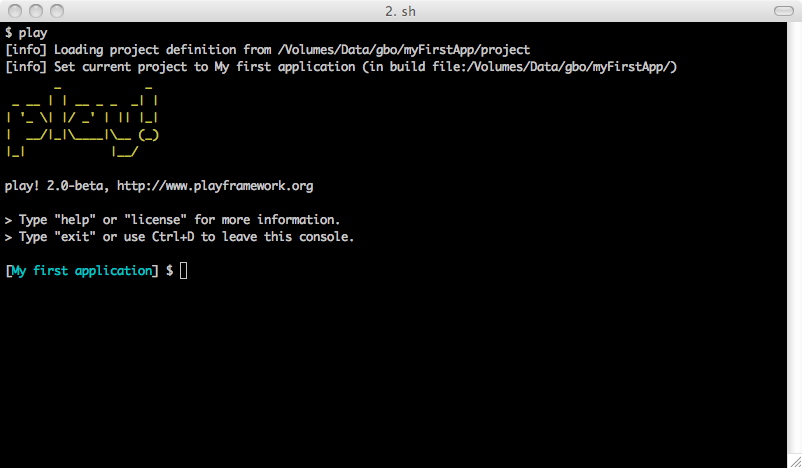
If you have installed Play using the standalone distribution, enter any existing Play application directory and run the play script:
$ cd /path/to/any/application
$ play
§Getting help
Use the help play command to get basic help about the available commands:
[My first application] $ help play
§Running the server in development mode
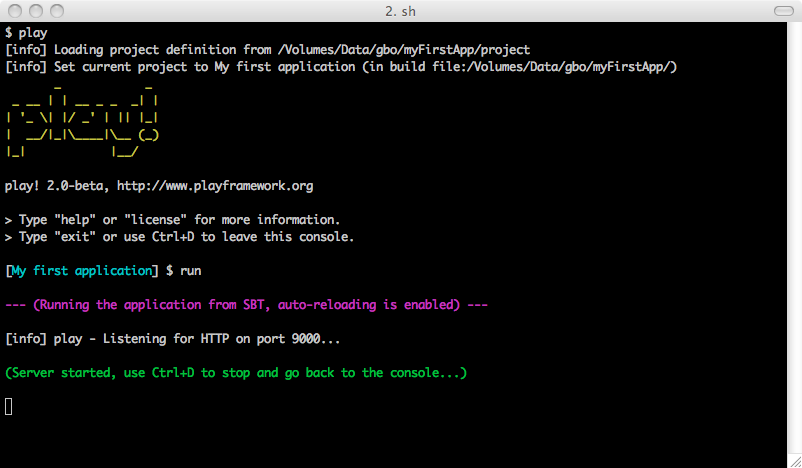
To run the current application in development mode, use the run command:
[My first application] $ run
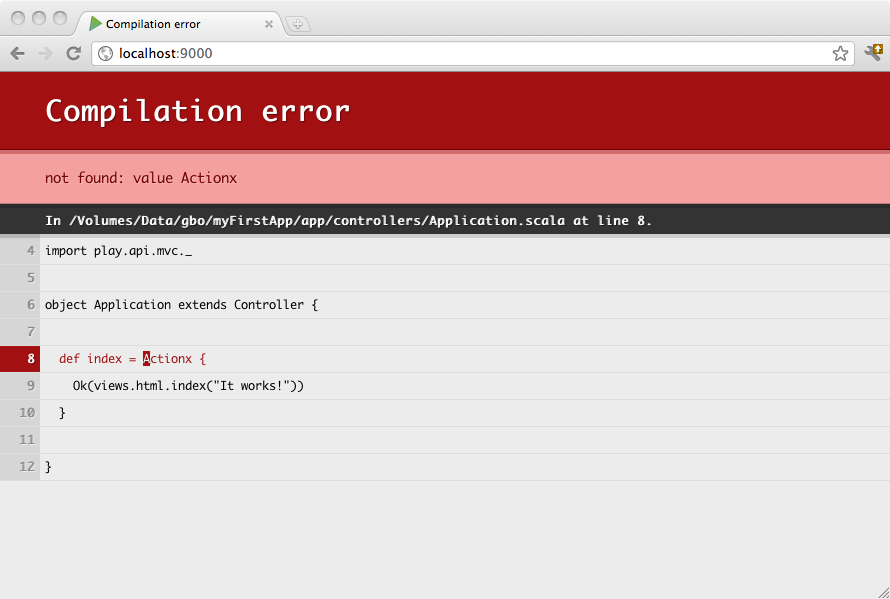
In this mode, the server will be launched with the auto-reload feature enabled, meaning that for each request Play will check your project and recompile required sources. If needed the application will restart automatically.
If there are any compilation errors you will see the result of the compilation directly in your browser:
To stop the server, type Crtl+D key, and you will be returned to the Play console prompt.
§Compiling
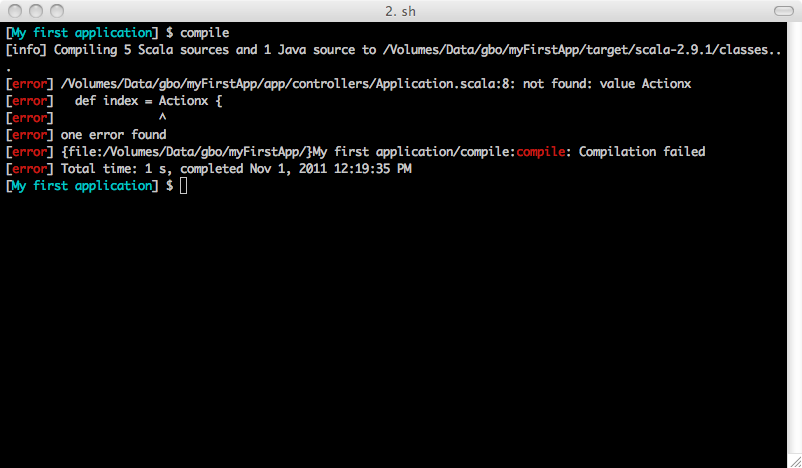
In Play you can also compile your application without running the server. Just use the compile command:
[My first application] $ compile
§Launch the interactive console
Type console to enter the interactive Scala console, which allows you to test your code interactively:
[My first application] $ console
To start application inside scala console (e.g to access database):
scala> new play.core.StaticApplication(new java.io.File("."))
§Debugging
You can ask Play to start a JPDA debug port when starting the console. You can then connect using Java debugger. Use the play debug command to do that:
$ play debug
When a JPDA port is available, the JVM will log this line during boot:
Listening for transport dt_socket at address: 9999
Note: Using
play debugthe JPDA socket will be opened on port9999. You can also set theJPDA_PORTenvironment variable yourself usingset JPDA_PORT=1234.
§Using sbt features
The Play console is just a normal sbt console, so you can use sbt features such as triggered execution.
For example, using ~ compile
[My first application] $ ~ compile
The compilation will be triggered each time you change a source file.
If you are using ~ run
[My first application] $ ~ run
The triggered compilation will be enabled while a development server is running.
You can also do the same for ~ test, to continuously test your project each time you modify a source file:
[My first application] $ ~ test
§Using the play commands directly
You can also run commands directly without entering the Play console. For example, enter play run:
$ play run
[info] Loading project definition from myFirstApp/project
[info] Set current project to My first application
--- (Running the application from SBT, auto-reloading is enabled) ---
[info] play - Listening for HTTP on port 9000...
(Server started, use Ctrl+D to stop and go back to the console...)
The application starts directly. When you quit the server using Ctrl+D, you will come back to your OS prompt.
§Force clean
If something goes wrong and you think that the sbt cache is corrupted, use the clean-all command for your OS command line to clean all generated directories.
$ play clean-all